Quantum dot marking technology to realize the trace of molecular motor in living cells
November 28, 2022
Single-molecule fluorescence tracer technology based on quantum dots is of great significance for studying the walking mode of molecular motor on the cytoskeleton in vitro. At present, the research on the motor characteristics of intracellular molecular motor is indirectly realized by tracing the organelles such as endocytosis and melanosome. These organelles are transported by molecular motors, so motion monitoring of the organelles can indirectly analyze the motion characteristics of the molecular motor. The Giovanni Cappello team at the University of Paris VI used quantum dot-labeled myosin V and delivered it into cells, recording myosin on the microfilament skeleton at a single cell level, with high temporal and high spatial resolution. Sports characteristics.
Paolo Pierobon and other purified calmodulin and biotin treatment, biotinylated calmodulin can be adsorbed to myosin, and then coupled with streptavidin by the binding properties of biotin-avidin (Streptavidin conjugated Quantum Dots, SA-QDs) combine to achieve quantum dot labeling of myosin (Figure 1). For quantum dot-labeled myosin, in vitro experiments confirmed that quantum dots did not affect myosin activity, and were then delivered into HeLa cells by changes in osmotic pressure, and images were acquired using a wide-field epifluorescence microscope (Fig. 2). Analysis, obtaining parameters such as stepping speed, step distance, dwell time and progressive distance of myosin, thus filling the gap in the in vivo study of motor molecules in living cells.
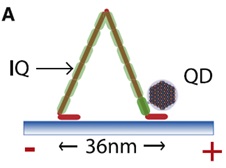 | Figure 1. Stepped pattern of myosin on the microfilament skeleton. A quantum dot (QD) is coupled to an IQ domain of myosin. |
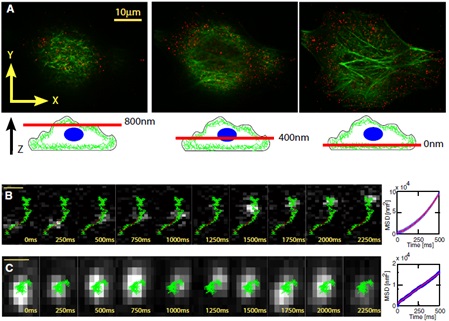
Figure 2 Tracing and analysis of myosin movement along the microfilament skeleton in Hela cells
(A) Quantum dot-labeled myosin (red highlights) is evenly distributed in the cells, and the microfilament skeleton is stained green by the Alexa Fluor 488-labeled phalloidin.
(B) Quantum dot-labeled myosin (silver-gray bright spots) orients along the microfilament skeleton (green).
(C) Quantum dot-labeled myosin (silver-gray bright spots) spread randomly in the cytoplasm.